
File |
The items in this menu can save your model or exit the program |
Load ModelSave ModelSave Screen To FileQuitHelp |
The items in this menu will give you information about how to use this program |
Getting StartedHow To Build A ModelControl DescriptionsMap Color DefinitionsAbout MigModelShow help in browserModel Settings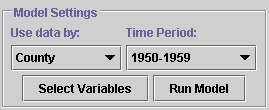 |
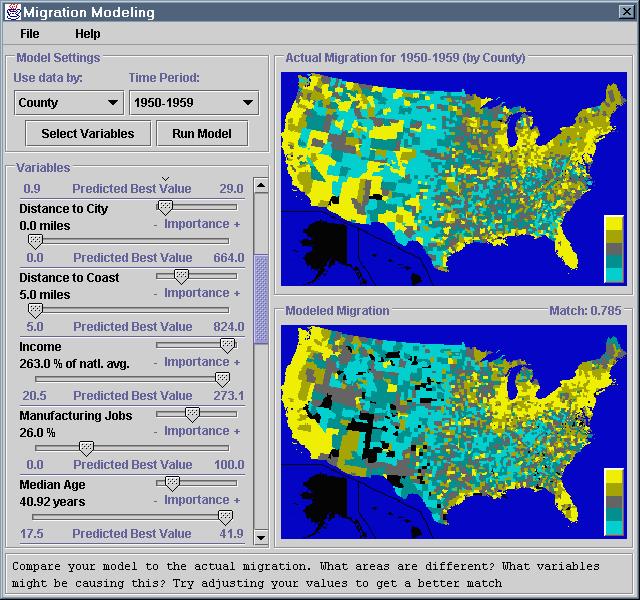
These control what statistics database your model will use, and allow you to set up your model and test it when it is completed |
Use data by:County or State
to get a list of time periods for which data of that type is available.
Time Period:Select Variables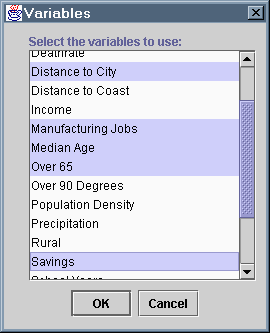 |
This buttons brings up a dialog that allows you to choose which statistics you
want to include in your model. You can select as many statistics as you want
from the list. To select an entire range of variables at once, click on the
first one in the range, then hold down Shift while clicking on
the last one in the range. To toggle whether or not a single variable is
selected, without changing the status of any of the others, hold down
Ctrl while clicking on that variable.
|
Run ModelVariables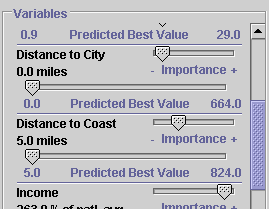 |
This is where you can view and edit your current model, by changing the
Predicted Best Value or Importance of each variable.
Each variable has a name, at the upper left, and a
Predicted Best Value right below that. There are two sliders, one
for adjusting the Predicted Best Value, and one for adjusting the
Importance of each variable
|
Predicted Best Value0.0 miles
for the Distance to City variable
ImportancePredicted Best Value for both the
Distance to City and Distance to Coast variables to
their minimum values, but set the Importance if the
Distance to Coast variable higher, then people would still tend to
migrate towards the coast, even if it was not near a city, while a fewer
number would migrate towards a city that was farther inland
Prev: How To Build A Model Next: Map Color Definitions